DISEASE
 Message of common value
Message of common value
Abnormal vessel growth because of too much oxygen after birth
THERE IS A GRAY LINE PRESENT IN THE TRANSITIONS AREA. HALFWAY THE RETINA THE BLOODVESSELS STOP GROWING
THERE EXCIST A WHITE WALL BY THE DEMARCATION LINE
GROWING OF ABNORMAL BLOODVESSELS IN THE VITREOUS
THERE EXCIST A RETINAL DETACHEMENT BECAUSE THE VITREOUS PULLS ON THE RETINA
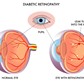
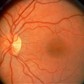
NORMAL ASPECT OF THE RETINA
THE RETINA LIES AT THE BACK OF THE EYE


DETAIL OF THE PALE SIDE. NORMALLY THE BLOODVESSELS HAVE TO GROW BY AFTER A STOP OF OXYGEN
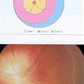

1e DANGER: THE NEW BLOODVESSELS CAN BLEED A LITTLE BIT OR VERY HARD
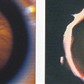
2TH DANGER: THE NEW BLOODVESSELS CAN SHRINK AND PULL OFF THE RETINA
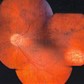
3TH DANGER: THE BLOODVESSELS CANGROW INTO SCARS. THAT LEADS TO A REDUCED VISION.
PREMATURE RETINOPATHY
This pathology is caused by the fact that the retina is constructed relatively LATE IN THE FETUS.
Due to lung problems, there isn't enough oxygen in the premature fase, so the blood vessels won't grow anymore.
The oxygen deficit is an angiogenic factor which causes new blood vessels in the area where mature retinal vessels pass into structures that are still immature.
The younger the premature, the bigger the immature zone (at 29 weeks, the maturation of the nasal side of the retina is ready / to 40 weeks (term = a) the maturing off the outer is complete).
Due to new blood vessels -who scarring quickly- causes TRACTION with retinal detachment.
The loose retina get STUCKED TO THE LENS center as a fibrous membrane, hence the former name of "retrolentale fibroplasy".
The retina problem is most common in very preterm infants (less than 32 weeks) and a very small weight (less than 1000 g: 80% get it / 1500 g: 10% get it) who gets oxygen for more than 3 days.
Especially the variations in OXYGEN CONCENTRATIONS ARE BAD, eg by bad lungs, open junctions between the aorta and pulmonary artery ("open ductus botali ") but also other diseases that increase the use of oxygen (eg infections): a child under 31 weeks and less than 1500 grams is best checked from the 6th week (and this untill the blood vessel ingrowth is normal)!
VARIOUS GRADATIONS
STAGE 0
Pale retina, with no ingrowth of vessels
STAGE I
White demarcation line, especially on the outer side of the retina (= further ingrowth of vessels was stopped) - creates 5 to 7 weeks after childbirth - a week can increase the severity. However, the injury usually takes off without leaving scars.
STAGE II
Elevated edge, by canalisation of the demarcation line - regularly occur as intraretinal new blood vessels on the outside of the edge especially alarming when it's about 5 or more clock hours clearly (freezing ("cryocoagulation ") of the injuries required)
STAGE III
New blood vessels grow into the vitreous. This is divided into three sub phases: mild, clear and serious. Freezing is urgently needed!
STAGE IV
Partial retinal detachment (with or without the macula (= central retina, responsible for analyzing the images). This is prognostically very unfavorable - classical retinal surgery may be tried.
STAGE V
Total retinal detachment. Vitreous surgery can still be tried, but seldom gives a good result (especially if the funnel, which the loose retina compose, is closed. Most likely it causes glaucoma, due to the shrinking in the posterior eye segment and the new blood vessels in the iris ( front of the eye). Prevention is better than therapy !
*** You can see these problems in different zones of the retina:
-zone 1: in the posterior pole, inside the big vessels
-zone 2: outside the big vessels
-zone 3: temporale perifery - these zone is most sensible to the problems
REMARKS
REMARK I
At each stage there can be a "plus". For example when there is abnormal convolution or swelling in the posterior pole vessels present, ev later combined with vitreous opacities (= by bleeding from new blood vessels), new blood vessels in the iris ("rubeosis iridis") and pupillary rigidity (don't get wide): still very alarming! - indicates a very active process!
REMARK II
Scars created by the retina problem:
CENTRAL
- Vessels: convolution / stretched over the course of the vessels
- Retina: displacement of the macula and folds
ON THE SIDE
- Vessels: abnormal branches / arcade / avascular areas
- Retina: thin zones, which give retinal detachment by the slightest injury/ folds / scar areas / zones of localized retinal detachment / membranes, which grow into the vitreous
Due to the scars high myopia arise regulary (possibly at one eye, if there is an asymmetry in the lesions) and therefore a lazy eye and strabismus (note: without a retinal problem strabismus appears also more by normal births) - for the best is ckeking preterm children with retinal problems every six months, in the scar stage.
IF YOU WANT A NEW LOOK
WE ARE HERE, TO HELP YOU
YOU AIN'T SEEN NOTHING YET
PRIORITY TO QUALITY
SHOW YOUR EYES, WITH LENSES!
GOOD LOOKING - GOOD SEEING
MORE INSIGHT IN YOUR SIGHT
PRIORITY TO QUALITY
WE LIKE TO "WOW" YOU
IF YOU WANT MORE
BETTER VISION - BETTER LOOKS